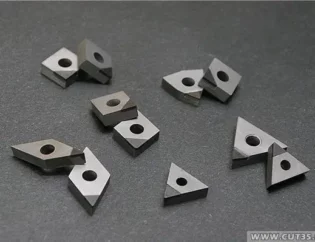
1.工具材料
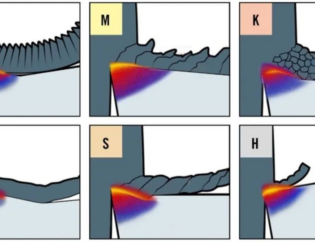
工具研削の一般的な工具材料は、高速度鋼、粉末冶金高速度鋼、超硬合金、PCD、CBN、サーメット、およびその他の超硬材料です。高速度鋼の工具は鋭くて丈夫ですが、超硬工具は硬度は高くなりますが靭性は低くなります。超硬工具の密度は、高速度鋼工具の密度よりも明らかに高くなっています。これら2つの材料は、ドリルビット、カッター、フライス、タップの主な材料です。 PM高速度鋼の特性は上記の2つの材料の間にあり、主に粗フライスとタップの製造に使用されます。
高速度鋼工具は、靭性が優れているため、衝突の影響を受けません。ただし、超硬工具は硬度と脆性が高く、衝突に敏感で、刃先が飛びやすい。したがって、研削の過程で、超硬工具の操作と配置は、切削工具間の衝突または切削工具の落下を防ぐために非常に注意する必要があります。
高速度鋼工具の精度が比較的低く、研削要件が高くなく、価格も高くないため、多くのメーカーが独自の工具ワークショップを設置して修理および研削を行っています。しかし、超硬工具は、多くの場合、研削のために専門の研削センターに送る必要があります。一部の国内工具研削センターの統計によると、修理のために送られた80%以上の工具は超硬工具です。

2.ツールグラインダー
工具の材質は非常に硬いため、研削でしか交換できません。切削工具の製造と研削において、一般的な工具研削盤は次のとおりです。
1)溝研削盤:ドリルビットやエンドミルなどの切削工具の溝または背面を研削します。
2)アングル研削盤:ドリルビットの円錐上角(または偏心後角)を研削します。
3)トリミング機:ドリルの横方向のエッジを修正します。
4)手動ユニバーサル工具研削盤:外円、溝、背面、上角、横方向エッジ、平面、すくい面などを研削します。少量で複雑な形状の工具によく使用されます。
5)CNCグラインダー:一般的に5軸リンケージ、機能はソフトウェアによって決定されます。ドリル、エンドミル、リーマーなど、大量かつ高精度の研削工具に一般的に使用されています。これらの研削盤の主なサプライヤーは、ドイツ、スイス、米国、オーストラリア、日本です。
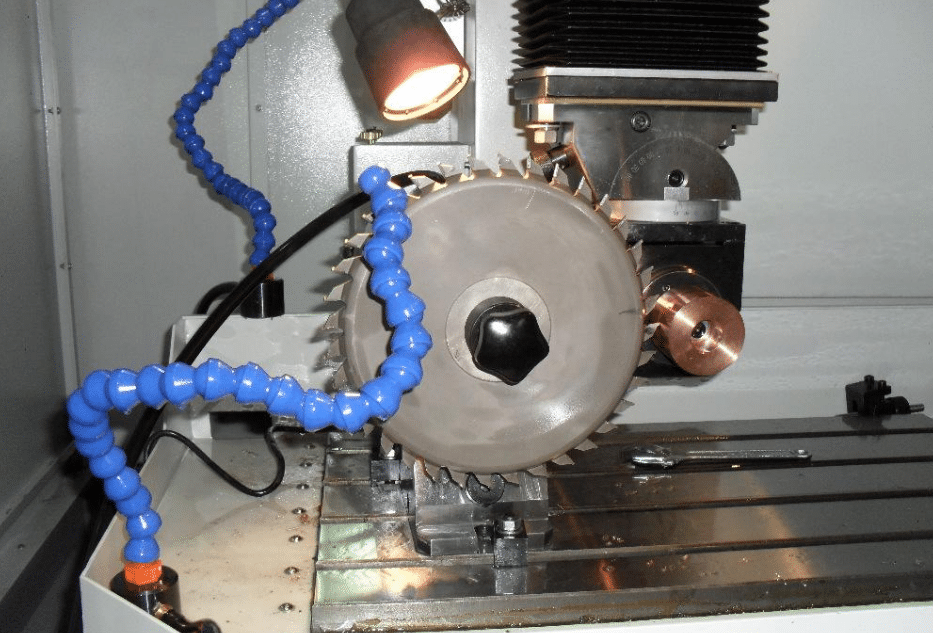
3.砥石
1)研磨剤
さまざまな材料の砥粒は、さまざまな種類の切削工具の研削に適しています。エッジ保護と加工効率の最良の組み合わせを保証するために、工具のさまざまな部分に必要な摩耗粒子サイズも異なります。
アルミナ:HSS工具の研削に使用されます。砥石は安価で、複雑な切削工具(コランダム)を研削するためにさまざまな形状に簡単に変更できます。
炭化ケイ素:CBN砥石とダイヤモンド砥石の修正に使用されます。
CBN(立方晶炭化ホウ素):HSS工具の研削に使用されます。高価格ですが、耐久性があります。国際的には、砥石はb107などのBで表され、107は砥粒径の大きさです。
ダイヤモンド:HM切削工具の研削に使用されます。高価格ですが、耐久性があります。砥石はd64などのDで表されます。ここで、64は研磨粒子の直径のサイズを表します。
2)形状
In order to facilitate the grinding of different parts of the cutter, the grinding wheel should have different shapes. The most commonly used are: parallel grinding wheel (1A1): grinding top angle, outer diameter, back, etc. Disc grinding wheel (12v9, 11v9): grinding spiral groove, milling cutter’s main and auxiliary cutting edge, trimming transverse edge, etc. After a period of use, the grinding wheel needs to modify its shape (including plane, angle and fillet R). In order to improve the grinding ability of the grinding wheel, the chip filling between the abrasive grains must be removed by using the cleaning stone frequently.
4.粉砕基準
Whether there is a set of good tool grinding standards is the standard to measure whether a grinding center is professional. In the grinding standard, the technical parameters of cutting edge of different cutting tools when cutting different materials are generally specified, including edge inclination angle, top angle, front angle, back angle, chamfering, etc. (in cemented carbide bits, the process of passivating the cutting edge is called “cutting edge”, and the width of the chamfered edge is related to the material to be cut, generally between 0.03 and 0.25 mm. The process of chamfering on the edge is called chamfering. Each professional company has its own grinding standards summarized for many years.
HMビットとHSSビットの違い:
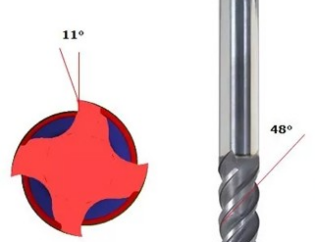
HSSビット:上部の角度は通常118度で、130度を超えることもあります。刃は鋭いです。精度の要件(エッジの高さの差、対称性、円周方向の振れ)は比較的低くなります。水平ブレードを修理する方法はたくさんあります。
HMビット:上部の角度は通常140度です。ストレートスロットドリルは多くの場合130度であり、スリーエッジドリルは通常150度です。刃先とエッジ(エッジ上)は鋭くなく、不動態化されることが多く、面取りと面取りと呼ばれます。横刃は、切りくずの破損を容易にするために、S字型にトリミングされることがよくあります。
Back angle: the back angle of the blade is very important to the tool. If the back angle is too large, the blade will jump easily and “stab the knife”; if the back angle is too small, the friction will be too large and the cutting will be unfavorable. The back angle of the tool varies with the material to be cut, the type of the tool and the diameter of the tool. Generally speaking, the rake angle decreases with the increase of tool diameter. In addition, if the material to be cut is hard, the back angle is smaller, otherwise, the rear angle is larger.
5.工具検出装置
工具検出装置は、一般に、工具設定装置、プロジェクター、ユニバーサル工具測定器の3つのカテゴリーに分類されます。工具設定装置は、主にマシニングセンタなどのCNC機器の工具設定準備(長さなど)に使用され、角度、半径、ステップ長などのパラメータの検出にも使用されます。プロジェクターの機能は、角度、半径、ステップ長などのパラメーターの検出にも使用されます。ただし、上記の2つの方法を使用して、工具のバックアングルを測定することはできません。ユニバーサルツール測定器は、バックアングルを含むツールのほとんどの幾何学的パラメータを測定できます。
したがって、工具専門の研削センターには、ユニバーサル工具測定器を装備する必要があります。しかし、この種の機器のサプライヤーは多くありません。市場にはドイツとフランスの製品があります。
6.グラインドメカニック
最高の機器はまた、人員によって操作され、研削技術者によって訓練される必要があります