Na produção diária, a escolha razoável do material e da forma da ferramenta de tornear afeta diretamente a produtividade do trabalho e a qualidade do processamento das peças. No processo de corte, a ferramenta deve suportar muita força de corte e força de impacto, e trabalhar a alta temperatura, e suportar continuamente forte atrito e extrusão, o que é fácil de causar desgaste e danos à ferramenta de torneamento. Se os materiais da ferramenta não forem selecionados razoavelmente, as peças não atenderão aos requisitos de uso, resultando em desperdício de material, danos prematuros das máquinas-ferramentas e equipamentos, resultando em grandes perdas econômicas. Portanto, diferentes materiais de ferramenta devem ser selecionados de acordo com diferentes materiais de usinagem. A seleção razoável de materiais para ferramentas de corte pode não apenas melhorar a eficiência da mão-de-obra e garantir a qualidade do processamento, mas também economizar custos e reduzir a intensidade da mão-de-obra dos trabalhadores.
Escolhas razoáveis de material da ferramentas
Os materiais para ferramentas incluem principalmente aço-ferramenta para carbono, aço-ferramenta para liga, aço de alta velocidade, carboneto cimentado, cerâmica e materiais para ferramentas super-duros.
Aço de ferramenta de carbono e aço de ferramenta de liga são usados principalmente na fabricação de ferramentas, matrizes e ferramentas de medição.
O aço de alta velocidade é um aço ferramenta com mais elementos de liga, como tungstênio (W), molibdênio (Mo), cromo (Cr) e vanádio (V). As ferramentas de aço de alta velocidade são fáceis de fabricar, fáceis de moer, fáceis de obter arestas vivas através da retificação e possuem boa tenacidade, que são frequentemente usadas nas ocasiões com grande força de impacto. É especialmente usado para fabricar várias ferramentas complexas de conformação e ferramentas de usinagem de furos. O aço de alta velocidade pode ser dividido em tungstênio e molibdênio de tungstênio. O aço de alta velocidade de tungstênio (W18Cr4V) é amplamente utilizado no momento, mas não pode ser usado no corte de alta velocidade devido à sua baixa resistência ao calor. O aço de alta velocidade e molibdênio de tungstênio (w6wo5cr4v2) é usado para fabricar ferramentas de laminação a quente, brocas helicoidais, etc.
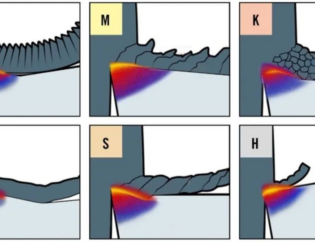
O carboneto cimentado é um tipo de metalurgia do pó, feito de pó de tungstênio e carboneto de titânio e cobalto como ligante e depois sinterizado a alta temperatura após prensagem a alta pressão. Atualmente, é o material de ferramenta de torneamento mais utilizado. De acordo com a composição, existem três tipos de liga de cobalto de tungstênio comumente usada (tipo K), liga de cobalto de tungstênio e titânio (tipo P) e liga de cobalto de tungstênio e titânio e tântalo (tipo M). Os carbonetos cimentados com cobalto e tungstênio são compostos por carboneto de tungstênio (WC) e cobalto (CO). Eles são usados principalmente para o processamento de ferro fundido, materiais quebradiços ou ocasiões com alto impacto. Os códigos comumente usados são K01, K10 e K20. Geralmente, K01 é usado para acabamento, K10 para semi-acabamento e K20 para usinagem em desbaste. O carboneto cimentado cobalto-titânio e tungstênio é composto por carboneto de tungstênio, cobalto e carboneto de titânio. É adequado para o processamento de aço ou outros materiais plásticos com alta tenacidade, mas é quebradiço, não é resistente a impactos e não é adequado para o processamento de materiais quebradiços. Os códigos comuns são P01, P10 e P30. Geralmente, P01 é usado para acabamento, P10 para semi-acabamento e P30 para usinagem em desbaste. Tungstênio, titânio, tântalo e cobalto são adequados para o processamento de metais ferrosos e não ferrosos com cavacos longos ou curtos. Os códigos comumente usados são M10 e M20. M10 é usado para acabamento e M20 é usado para usinagem em desbaste. As ferramentas de corte em cerâmica são usadas principalmente para semi-acabamento e acabamento de metais não ferrosos, ferro fundido e aço temperado. Os materiais super-duros são nitreto cúbico de boro e Diamante: o nitreto cúbico de boro é usado para semi-acabamento e acabamento de ligas, aço temperado e ferro fundido resfriado. O diamante pode cortar com precisão metais não ferrosos e ligas e materiais resistentes ao desgaste com alta dureza.
Seleção do cortador de rosqueamentos
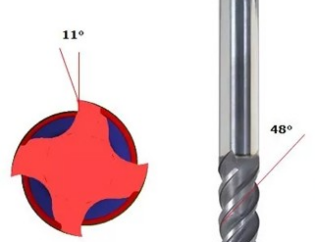
A seleção da ferramenta de torneamento de rosca é amplamente utilizada em todos os tipos de produtos mecânicos, e as peças com rosca e sem-fim são amplamente utilizadas. As ferramentas de torneamento de roscas com ângulos diferentes são selecionadas de acordo com diferentes roscas.
(1) there are two kinds of triangular thread turning tools: high speed steel and hard alloy. The high-speed steel thread turning tool has the advantages of convenient grinding, easy sharpening, good toughness, not easy to crack the tip of the tool, small surface roughness value of the thread, but poor heat resistance, which is only suitable for low-speed thread turning. Hard alloy thread turning tool has high hardness, good wear resistance, high temperature resistance, good thermal stability, but poor impact resistance. Therefore, carbide thread turning tool is suitable for high speed cutting. In high-speed cutting, the actual profile will be enlarged, so the sharp angle of the tool should be reduced by about 30 ‘, and the roughness of the front and back face of the turning tool must be very small.
(2) when turning trapezoidal thread, the radial cutting force is large. In order to reduce the cutting force, it can be divided into rough turning and finish turning. During rough turning, in order to facilitate left and right cutting and reserve the finishing allowance, the width of the cutter head shall be smaller than the width of the bottom of the alveolar, the back angle of the diameter shall be about 8 °, the front angle shall be 10 ° – 15 °, the back angle of both sides shall be (3 ° – 5 °) ± ψ (thread rising angle), and the tooth angle shall be 30 ° 0 – 30 ′. The front angle of high-speed steel finishing tool diameter is 0, and the angle between the cutting edges on both sides is equal to the tooth angle. In order to ensure the smooth cutting on both sides of the cutting edge, the cutting edge should be grinded with a large rake angle (10 ° – 16 °). However, it must be noted that the cutting edge at the front end of the turning tool cannot participate in the cutting. The high-speed steel ladder thread turning tool can process the thread with high precision and small surface roughness, but the production efficiency is low. In order to improve production efficiency, carbide turning tools can be used for high-speed cutting when turning general precision threads.
(3) there are two kinds of commonly used worm: metric (20 °) and British (14.5 °). British worm is rarely used in China. Metric worm is mainly used. High speed steel turning tool is generally used for worm turning, and rough turning and fine turning are used for turning. During rough turning, it is required that the included angle between the cutting edges on the left and right sides is slightly less than twice the tooth shape angle, the width of the cutter head is less than the width of the tooth root slot, the left and right radial front angles of 10 ° ~ 15 ° are ground, the back angles of both sides are (3 ° ~ 5 °) ± ψ, and the cutter tip is properly rounded. When finishing, the included angle between the left and right edges is equal to twice of the tooth shape angle and should be symmetrical. The straightness of the cutting edge is better, the surface roughness value is small, and the chip rolling groove with large front angle (15 ° – 20 °) is ground. The above are only some basic ideas for the selection of turning tool materials and shapes. Due to the wide variety of cutting tools, the structural types and processing requirements of parts vary greatly. In practical operation, there is still a need for experience. Skilled personnel conduct scientific analysis based on the production conditions of schools and enterprises (production, planning, production compactness, scale, capital, etc.) and the conditions of processing parts and equipment, and select the cutting tools with reasonable performance and price, In this way, we can give full play to the potential of the equipment, ensure the processing quality, improve the processing efficiency, and improve the experience and efficiency of the enterprise.