What Is Sintering?
Before diving into Sinter HIP, let’s first introduce sintering. Sintering is a process by which materials are compacted using high pressure and heat. It is used to make high-tech materials and improves their mechanical properties. Sintering is used for a variety of purposes, from making structural steel parts to porous metals and magnetic materials.
Sintering is an important process used in manufacturing and is often used in combination with other processes. The process of fusing metal powders is called “sintering” and involves applying heat and pressure to solidify a powder. Because the process does not melt the material, sintering can be used for a variety of purposes. Metal powders are often sintered to improve their strength.
There are two types of sintering: solid state sintering and liquid phase sintering. The former involves mixing the raw materials and adding a liquid additive. Liquid phase sintering is similar to solid state sintering, but it involves adding a liquid substance to the powder. This helps the liquid to move through the powder’s pores and join the solid particles together.
Carboneto de tungstênio is a common example of sintered materials. These materials are used in all kinds of products, from carbide wear parts to cutting tools.
What Is Sinter HIP?
Sinter-HIP is a process that uses high temperatures and gas pressure to compact a powder material. The pressure is uniform and applied to the powders in all directions. This process reduces porosity in manufactured components and helps improve properties like toughness and corrosion resistance. This process uses less gas pressure than conventional hot isostatic pressing(HIP), which limits their density and porosity.
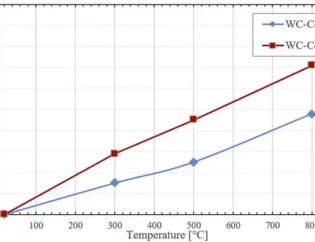
The sinter-HIP process aims to obtain a final temperature of 1400 degrees Celsius. It is similar to the conventional sintering cycle, which was carried out at a temperature of 1450 degrees Celsius. Thanks to the high pressure during the HIP sintering process, the needed temperature was lower than traditional sintering so it is more efficient and environmentally friendly. This process is widely used in making ultra-fine tungsten carbide material.
Sinter HIP process
Sinter-HIP, also called HIP sintering, is a process that utilizes high isostatic pressure to form materials at elevated temperatures. High pressure induces densification through a variety of mechanisms, including material deformation, creep, and diffusion. Material deformation is the dominant driving mechanism, but the other mechanisms contribute to densification by closing pores and eliminating defects.
Application of Sinter HIP
Sinter-HIP can be designed to meet specific applications. They can convert powders to fully dense products and eliminate porosity in sintered products. The temperature and pressure of HIP processes can range from around 1100degC for powder consolidation of PM tool steels to over 2000degC for ceramics. The entire process can last for several hours.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, hip sintering is also advantageous for the manufacture of structural and nonstructural components. The process is cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing processes.
HIP is an increasingly popular method for the production of high-performance structural components. The process can be used for casting defect repair, the consolidation of ceramic and powder metal parts, and diffusion bonding. HIP also eliminates voids in a component’s surface. A variety of industrial gases are used in the HIP process. Hydrogen is used to facilitate the removal of the binder material, while argon provides a pressure medium for densification and void removal.
Hip sintering furnaces are currently in wide use throughout aerospace, defense, oil & gas, electronics, and marine industries. Their design features enable the processing of super alloys.
Sinter HIP Furnace
A Sinter HIP furnace typically consists of a high-temperature resistive heating furnace, a gas-handling system, and auxiliary equipment. Modern HIP units have computers that allow the user to program cycles and optimize processing parameters. The equipment consists of a pressure vessel, a high-temperature resistive heating furnace, and an electrical and gas-handling system.
HIP sintering furnaces can be very efficient. They can develop a vacuum environment and high pressure at the same time, saving a lot of time and money. They can also produce components with consistent geometries. If this type of furnace is right for your application, it can increase the productivity of the process while saving costs.

Conclusão
With Sinter-HIP Furnace, we can apply the sintering process with high pressure in order to eliminate porosity and improve the properties of our products. Almost all tungsten carbide products from Meetyou are made using this technology in order to maintain our pursuit of high quality.