In der täglichen Produktion wirkt sich die vernünftige Wahl des Drehwerkzeugmaterials und der Form direkt auf die Arbeitsproduktivität und die Bearbeitungsqualität der Teile aus. Beim Schneiden muss das Werkzeug viel Schneidkraft und Schlagkraft aushalten, bei hoher Temperatur arbeiten und kontinuierlich starke Reibung und Extrusion aushalten, was leicht zu Verschleiß und Beschädigung des Drehwerkzeugs führen kann. Wenn die Werkzeugmaterialien nicht vernünftig ausgewählt werden, erfüllen die Teile nicht die Verwendungsanforderungen, was zu Materialverschwendung, vorzeitiger Beschädigung von Werkzeugmaschinen und Ausrüstung führt, was zu großen wirtschaftlichen Verlusten führt. Daher sollten unterschiedliche Werkzeugmaterialien entsprechend unterschiedlichen Bearbeitungsmaterialien ausgewählt werden. Eine vernünftige Auswahl von Schneidwerkzeugmaterialien kann nicht nur die Arbeitseffizienz verbessern und die Verarbeitungsqualität sicherstellen, sondern auch Kosten sparen und die Arbeitsintensität der Arbeiter verringern.
Angemessene Auswahl des Werkzeugmaterialss
Zu den Werkzeugmaterialien gehören hauptsächlich Kohlenstoff-Werkzeugstahl, legierter Werkzeugstahl, Schnellarbeitsstahl, Hartmetall, Keramik und superharte Werkzeugmaterialien.
Kohlenstoff-Werkzeugstahl und legierter Werkzeugstahl werden hauptsächlich zur Herstellung von Werkzeugen, Matrizen und Messwerkzeugen verwendet.
Schnellarbeitsstahl ist ein Werkzeugstahl mit mehr Legierungselementen wie Wolfram (W), Molybdän (Mo), Chrom (Cr) und Vanadium (V). Hochgeschwindigkeitsstahlwerkzeuge sind einfach herzustellen, leicht zu schleifen, durch Schleifen leicht scharfe Kanten zu bekommen und haben eine gute Zähigkeit, die häufig bei Gelegenheiten mit großer Schlagkraft verwendet werden. Es wird insbesondere zur Herstellung verschiedener komplexer Umformwerkzeuge und Lochbearbeitungswerkzeuge verwendet. Schnellarbeitsstahl kann in Wolfram und Wolfram-Molybdän unterteilt werden. Wolfram-Schnellarbeitsstahl (W18Cr4V) ist derzeit weit verbreitet, kann aber aufgrund seiner geringen Hitzebeständigkeit nicht beim Hochgeschwindigkeitsschneiden verwendet werden. Wolfram-Molybdän-Schnellarbeitsstahl (w6wo5cr4v2) wird zur Herstellung von Warmwalzwerkzeugen, Spiralbohrern usw. verwendet.
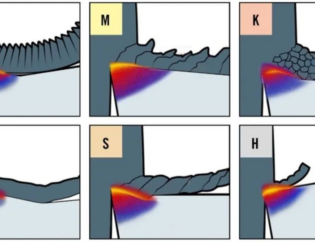
Hartmetall ist eine Art Pulvermetallurgieprodukt, das aus Wolfram- und Titankarbidpulver und Kobalt als Bindemittel hergestellt und nach dem Hochdruckpressen bei hoher Temperatur gesintert wird. Es ist derzeit der am weitesten verbreitete Drehmeißelwerkstoff. Entsprechend der Zusammensetzung gibt es drei Arten von üblicherweise verwendeten Wolfram-Kobalt-Legierungen (K-Typ), Wolfram-Titan-Kobalt-Legierungen (P-Typ) und Wolfram-Titan-Tantal-Kobalt-Legierungen (M-Typ). Wolfram-Kobalt-Hartmetalle bestehen aus Wolframcarbid (WC) und Kobalt (CO). Sie werden hauptsächlich zur Bearbeitung von Gusseisen, spröden Materialien oder Anlässen mit hoher Schlagkraft eingesetzt. Häufig verwendete Codes sind K01, K10 und K20. Im Allgemeinen wird K01 zum Schlichten, K10 zum Vorschlichten und K20 zum Schruppen verwendet. Wolfram-Titan-Kobalt-Hartmetall besteht aus Wolframcarbid, Kobalt und Titancarbid. Es eignet sich für die Bearbeitung von Stahl oder anderen Kunststoffen mit hoher Zähigkeit, ist jedoch spröde, nicht schlagzäh und nicht für die Bearbeitung von spröden Materialien geeignet. Gängige Codes sind P01, P10 und P30. Im Allgemeinen wird P01 zum Schlichten, P10 zum Vorschlichten und P30 zum Schruppen verwendet. Wolfram, Titan, Tantal und Kobalt eignen sich für die Bearbeitung von Eisen- und Nichteisenmetallen mit langen oder kurzen Spänen. Häufig verwendete Codes sind M10 und M20. M10 wird zum Schlichten und M20 zum Schruppen verwendet. Keramische Schneidwerkzeuge werden hauptsächlich zum Halbschlichten und Schlichten von Nichteisenmetallen, Gusseisen und gehärtetem Stahl verwendet. Die superharten Materialien sind kubisches Bornitrid und Diamant: kubisches Bornitrid wird zum Halbschlichten und Schlichten von Legierungen, gehärtetem Stahl und Hartguss verwendet. Diamant kann Nichteisenmetalle und -legierungen sowie verschleißfeste Materialien mit hoher Härte präzise schneiden.
Auswahl des Gewindeschneiderss
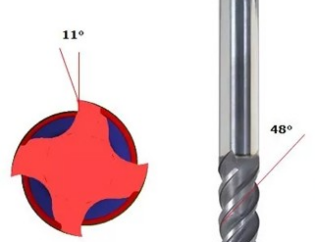
Die Auswahl an Gewindedrehwerkzeugen ist in allen Arten von mechanischen Produkten weit verbreitet, und die Teile mit Gewinde und Schnecke sind weit verbreitet. Die Gewindedrehwerkzeuge mit unterschiedlichen Winkeln werden nach unterschiedlichen Gewinden ausgewählt.
(1) there are two kinds of triangular thread turning tools: high speed steel and hard alloy. The high-speed steel thread turning tool has the advantages of convenient grinding, easy sharpening, good toughness, not easy to crack the tip of the tool, small surface roughness value of the thread, but poor heat resistance, which is only suitable for low-speed thread turning. Hard alloy thread turning tool has high hardness, good wear resistance, high temperature resistance, good thermal stability, but poor impact resistance. Therefore, carbide thread turning tool is suitable for high speed cutting. In high-speed cutting, the actual profile will be enlarged, so the sharp angle of the tool should be reduced by about 30 ‘, and the roughness of the front and back face of the turning tool must be very small.
(2) when turning trapezoidal thread, the radial cutting force is large. In order to reduce the cutting force, it can be divided into rough turning and finish turning. During rough turning, in order to facilitate left and right cutting and reserve the finishing allowance, the width of the cutter head shall be smaller than the width of the bottom of the alveolar, the back angle of the diameter shall be about 8 °, the front angle shall be 10 ° – 15 °, the back angle of both sides shall be (3 ° – 5 °) ± ψ (thread rising angle), and the tooth angle shall be 30 ° 0 – 30 ′. The front angle of high-speed steel finishing tool diameter is 0, and the angle between the cutting edges on both sides is equal to the tooth angle. In order to ensure the smooth cutting on both sides of the cutting edge, the cutting edge should be grinded with a large rake angle (10 ° – 16 °). However, it must be noted that the cutting edge at the front end of the turning tool cannot participate in the cutting. The high-speed steel ladder thread turning tool can process the thread with high precision and small surface roughness, but the production efficiency is low. In order to improve production efficiency, carbide turning tools can be used for high-speed cutting when turning general precision threads.
(3) there are two kinds of commonly used worm: metric (20 °) and British (14.5 °). British worm is rarely used in China. Metric worm is mainly used. High speed steel turning tool is generally used for worm turning, and rough turning and fine turning are used for turning. During rough turning, it is required that the included angle between the cutting edges on the left and right sides is slightly less than twice the tooth shape angle, the width of the cutter head is less than the width of the tooth root slot, the left and right radial front angles of 10 ° ~ 15 ° are ground, the back angles of both sides are (3 ° ~ 5 °) ± ψ, and the cutter tip is properly rounded. When finishing, the included angle between the left and right edges is equal to twice of the tooth shape angle and should be symmetrical. The straightness of the cutting edge is better, the surface roughness value is small, and the chip rolling groove with large front angle (15 ° – 20 °) is ground. The above are only some basic ideas for the selection of turning tool materials and shapes. Due to the wide variety of cutting tools, the structural types and processing requirements of parts vary greatly. In practical operation, there is still a need for experience. Skilled personnel conduct scientific analysis based on the production conditions of schools and enterprises (production, planning, production compactness, scale, capital, etc.) and the conditions of processing parts and equipment, and select the cutting tools with reasonable performance and price, In this way, we can give full play to the potential of the equipment, ensure the processing quality, improve the processing efficiency, and improve the experience and efficiency of the enterprise.