With the improvement of people’s quality of life, the requirements of product aesthetics and quality are also rising. More and more consumer products are made of alloy materials. Metal materials give people a sense of high-end, solid and durable quality, while traditional plastic shell products are gradually labeled as “cheap” and “low quality” in the hearts of consumers.
For consumer products, the commonly used alloy materials are aluminum alloy, zinc alloy and magnesium alloy. Titanium alloy is often used in medical field because of its good biocompatibility. Fang Gong will take a look at the characteristics of these alloy materials and make a comparison.
Therefore, the inductive summary is put in the front, as shown in the following performance comparison table.
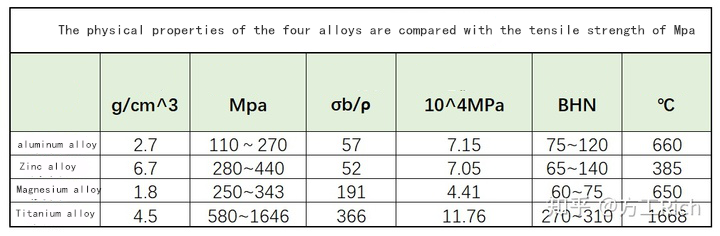
Comparison table of physical properties
Among the four alloys, titanium alloy is the hardest and has the best strength. In terms of hardness, titanium alloy is much harder than the other three alloys. In terms of tensile strength, titanium alloy is stronger than zinc alloy, followed by magnesium alloy, and aluminum alloy has the lowest strength.

Strength and hardness comparison
However, in terms of product structure design, weight should also be taken into account. If the specific gravity is taken into account, the specific strength of zinc alloy will be the minimum due to the maximum density. Titanium alloy and magnesium alloy have high specific strength, but titanium alloy is expensive and has poor processability. Therefore, magnesium alloy is often used in the structural parts that need to comprehensively consider the weight and strength.
aluminium alloy
The ingredients of the materials can be found directly in Du Niang. It doesn’t take much time to list them here. The density of aluminum alloy is 2.63-2.85g/cm, and it has high strength( σ B is 110-270mpa), the specific strength is close to that of high alloy steel, and the specific stiffness is higher than that of steel. It has good casting performance, plastic processing performance, good electrical and thermal conductivity, good corrosion resistance and weldability.
The fluidity of die casting aluminum alloy is good, and the melting point is 660 ℃.
Aluminum alloy has the most abundant application forms in product structure design. The common processing technologies include die casting, extrusion, machining, stamping and forging. Aluminum alloy profiles are widely used in building doors and windows, and aluminum profiles are often used to build frames for mechanical equipment. There is no lack of aluminum alloy in the shell of electronic products and consumer goods. This kind of products have higher appearance requirements, and the more common processes are extrusion, machining, stamping, etc.
Die casting aluminum is seldom used in the shell of FMCG. Because die casting aluminum alloy contains high content of Si, it reacts directly with the solution when anodizing, and the surface effect after oxidation is poor. Aluminum castings are often used in internal structural parts and parts with low appearance requirements. The motorcycle engine shell needs complex structure, light weight and enough strength. Most of the rotary aluminum alloy die casting is used as blank.
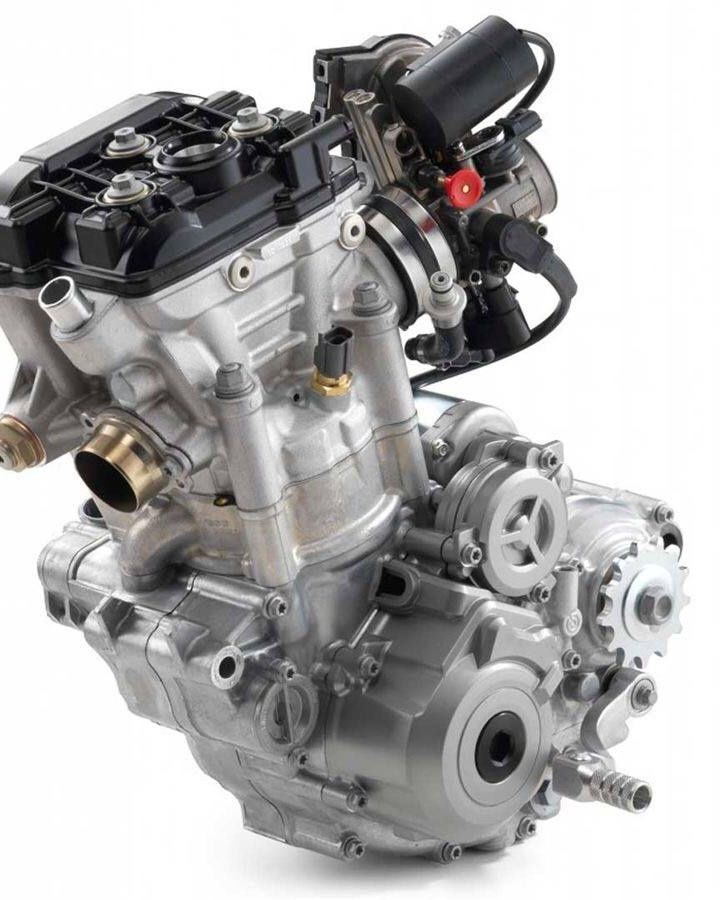

Aluminum cast engine housing
Aluminum grade:
one ××× The series is pure aluminum (the aluminum content is not less than 99.00%), and the last two digits of the series mark are expressed as percentage points of the minimum aluminum content. The second letter of the brand indicates the modification of the original pure aluminum.
two ×××~ eight ××× The last two digits of the series are of no special significance and are used only to distinguish: different aluminium alloys in the same group. The second letter of the brand indicates the modification of the original pure aluminum.
two ××× Series: aluminum alloy with copper as the main alloy element. 2011 fast cutting alloy, good cutting strength is also high. The alloy for forging in 2218, 2018 has good forging property and high temperature strength.
three ××× Series: aluminum alloy with manganese as main alloy element. 31053105 building materials, color aluminum plate, bottle cap.
four ××× Series: aluminum alloy with silicon as main alloy element. 4032 has good heat resistance, friction resistance and cancellation, and has a small coefficient of thermal expansion. Piston, cylinder head.
five ××× Series: aluminum alloy with magnesium as the main alloy element. 5052 is the most representative alloy with medium strength, and is generally sheet metal, ship, vehicle, building, bottle cap and honeycomb board.
six ××× The series are: aluminum alloy with magnesium as the main alloy element and Mg2Si as the strengthening phase. 6063 representative extrusion alloy has low strength than 6061 and good extrusion property. It can be used as a complex profile material with good corrosion resistance and surface treatment. It is good for building, highway guardrail, high fence, vehicle, furniture, household appliances and decoration.
seven ××× Series: aluminum alloy with zinc as main alloy element. One of the most powerful alloys in 7075 aluminum alloy is poor corrosion resistance. The coating material of 7072 can improve its corrosion resistance, but the cost is improved. Aircraft, ski stick.
eight ××× Series: aluminum alloy with other elements as main alloy elements
nine ××× Series: spare alloy group
Aluminum alloy with tensile strength greater than 480mpa is called high strength aluminum alloy, mainly based on Al Cu mg and Al Zn mg Cu, namely, 2XXX (hard aluminum alloy) and 7xxx (super hard aluminum alloy) alloy. The static strength of the former is slightly lower than that of the latter, but the temperature is higher than that of the latter. The properties of the alloy are different due to the different chemical composition, melting and solidification methods, processing technology and heat treatment system.
Zinc alloy has low melting point, good fluidity and easy to be welded. According to the manufacturing process, it can be divided into casting zinc alloy and deformed zinc alloy. The casting zinc alloy has good fluidity and corrosion resistance, and is suitable for die casting instruments, automobile parts shell, etc. The deformed zinc alloy has good plasticity and ductility, mainly used as battery shell, printing board, roof panel and daily hardware. The yield of casting alloy is much larger than that of deformed alloy. For the structural parts of quick dissipation, deformation alloy is rarely used. So the following is only for die-casting zinc alloy.
The density of zinc alloy is 6.3-6.7g/cm, and the tensile strength σ B is 280-440mpa, with low melting point, melting at 385 ℃, easy to die-casting.
Zinc alloy ratio is significant, which is the largest proportion of the four alloys described in this paper, and the fluidity is the best. It has good casting performance, and can die-casting precision parts with complex shape and thin-walled, and the surface of the casting is smooth. Among the products I designed, the thickness of the thin-walled zinc alloy die casting is only 0.4mm.
The strength of zinc alloy is good at room temperature. It is important to note that zinc alloy should not be used in high temperature and low temperature (below 0 ℃), and zinc alloy has good mechanical properties at room temperature. But the tensile strength and impact performance of the two groups decreased significantly at high temperature. The corrosion resistance of zinc alloy is poor. When the impurity elements lead, cadmium and tin exceed the standard, the casting will be deformed due to aging. The aging effect and aging phenomenon exist in zinc alloy die casting, that is, the strength naturally decreases after a long time and becomes brittle. This is what many people make complaints about when they change the zinc alloy faucet. They often break down, causing the tap part to remain in the water pipe. Therefore, the square workers still suggest that we try to choose copper faucets when decorating, do not choose zinc alloy.
At present, there are two kinds of standard series used as castings in the world, one is Zamak alloy and the other is Za series alloy. Zamak alloys used are Zamak 2, Zamak 3, zamak5 and Zamak 7( For convenience, the above alloys are alloy 2, 3, 5 and 7). Za series are za-8, ZA-12, ZA-27 and za-35. Za-8 is mainly used for hot chamber die casting. ZA-12 and ZA-27 can only be used for cold chamber die casting because of special melting requirements. Za-35 is generally used in gravity casting. The development of Zamak alloy is prior to Za series alloy and is mainly used in pressure casting. The most widely used is No. 3 zinc alloy.
Zamak 2: it is used for mechanical parts with special requirements for mechanical properties, high hardness requirements, good wear resistance and general dimensional accuracy requirements.
Zamak 3: good fluidity and mechanical properties. It is used for castings with low mechanical strength, such as toys, lamps, decorations and some electrical parts.
Zamak 5: good fluidity and good mechanical properties. It is used for castings with certain requirements for mechanical strength, such as automobile parts, mechanical and electrical parts, mechanical parts and electrical components.
Za8: it has good impact strength and dimensional stability, but it has poor fluidity. It is applied to die casting parts with small size, high precision and high mechanical strength, such as electrical parts.
Super oy: the best fluidity is applied to die casting thin-walled, large-size, high precision and complex shape workpieces, such as electrical components and box bodies.
magnesium alloy
Magnesium alloy is an alloy which is based on magnesium and other elements. The main alloy elements are aluminum, zinc, manganese, cerium, thorium and a small amount of zirconium or cadmium. At present, magnesium aluminum alloy is the most widely used, followed by magnesium manganese alloy and magnesium zinc alloy. Magnesium alloy can be widely used in automobile, electronics, textile, architecture and military fields because of its excellent casting, extrusion, cutting and bending processing.
The melting point of magnesium alloy is 650 ℃, and the melting point is lower than that of aluminum alloy, and the die casting performance is good. The tensile strength of magnesium alloy castings is equivalent to that of aluminum alloy castings, generally up to 250Mpa and up to 600 MPa.
Magnesium alloy has a low density (about 1.8g/cm3) and high strength. Magnesium alloy is the lightest metal structure material, with a specific gravity of 1.8, which is 2/3 of aluminum and 1/4 of iron, and its specific strength is 133, which makes magnesium alloy available as high strength material. The specific strength of high strength magnesium alloy can even be compared with titanium.
The elastic modulus of magnesium alloy is large and the seismic resistance is good. In the elastic range, the energy absorbed by magnesium alloy is half larger than that of aluminum alloy when it is under impact load, so magnesium alloy has good anti-seismic noise reduction performance.
Magnesium alloy has good die casting properties, and the minimum wall thickness of die casting can reach 0.5mm, which is suitable for manufacturing various kinds of automobile die castings. Magnesium alloy parts have high stability, high precision of casting size, and can be machined with high precision.
The heat dissipation of magnesium alloy has absolute advantage compared with that of alloy. For the radiator of magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy material of the same volume and shape, the heat produced by a heat source (temperature) magnesium alloy is more easily transferred from the root of the heat sink to the top than that of aluminum alloy, and the top is more tolerant to high temperature.
But the linear expansion coefficient of magnesium alloy is very large, reaching 25-26 μ M/m ℃, while aluminum alloy is 23 μ M/m ℃, brass about 20 μ M/m ℃, structural steel 12 μ M/m ℃, cast iron about 10 μ M/m ℃, rock (granite, marble, etc.) is only 5-9 μ M/m ℃, glass 5-11 μ m/m℃。 When applied to heat source, the influence of temperature on structure size must be considered.
Magnesium alloy application example: generally high-end and professional digital SLR cameras adopt magnesium alloy as the skeleton, making it durable and good in hand; Mobile phone, the case of laptop; Magnesium alloy is used on the shell and heat dissipation parts of the computer and projector which produce high temperature inside; The structure parts of steering wheel, steering bracket, brake support, seat frame, mirror support and distribution bracket require light weight and high strength.
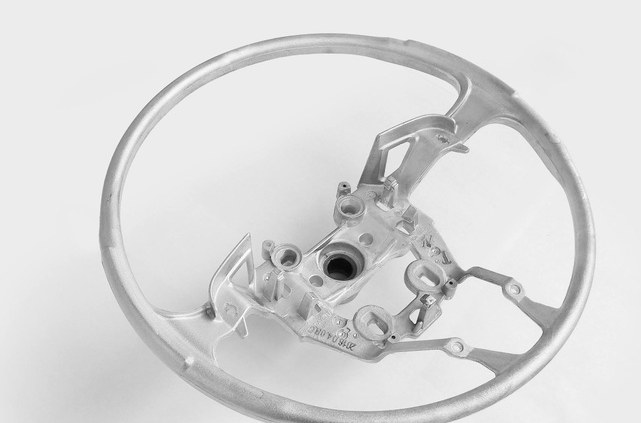
Magnesium alloy die casting steering wheel framework
According to the forming method, it can be divided into wrought magnesium alloy and cast magnesium alloy.
Magnesium alloy grade is expressed in the form of English letters + numbers + English letters. The front English letters are the codes of the most important alloy elements (the element codes are specified in the table below), and the following numbers represent the average values of the upper and lower limit values of the most important alloy elements. The last English letter is the identification code, which is used to identify different alloys with different specific constituent elements or slightly different element contents.
The common grades of magnesium alloys are AZ31B, az31s, az31t, az40m, az41m, AZ61A, az61m, az61s, az62m, AZ63B, AZ80A, az80m, az80s, AZ91D, AM60B, AM50A, M1c, M2M, M2S, ZK61M, zk61s, ME20M, LZ91, lz61, lz121, la141, la191, laz933, la81, la91, laz931, ma18, ma21, ma14, etc.
titanium alloy
Titanium alloy refers to a variety of alloy metals made of titanium and other metals, with high strength, good corrosion resistance and high heat resistance. Titanium alloy is widely used in the manufacture of aircraft engine compressor components, framework, skin, fasteners and landing gear. Titanium alloys are also used in rocket, missile and high-speed aircraft structures.
Titanium is an isomer with a melting point of 1668 ℃ and a close packed hexagonal lattice structure below 882 ℃ α Titanium; It has a body centered cubic lattice structure above 882 ℃, which is called the β Titanium. According to the different characteristics of the above two structures of titanium, the titanium alloys with different microstructures can be obtained by adding appropriate alloying elements. At room temperature, titanium alloys have three kinds of matrix structures, and they can be divided into the following three types: α Alloy( α+β) Alloys and β Alloy. China is represented by TA, TC and TB respectively.
The density of titanium alloy is generally about 4.51g/cm3, which is only 60% of steel. Some high-strength titanium alloys exceed the strength of many alloy structures. Therefore, the specific strength (strength / density) of titanium alloy is much higher than that of other metal structural materials, which can produce parts with high unit strength, good rigidity and light weight.

Titanium alloy products
Titanium is nontoxic, light, high strength and biocompatible. It is an ideal medical metal material and can be used as an implant in human body. In the United States, there are five β Titanium alloys are recommended to the medical field, i.e. tmzftm (ti-12mo – ^ zr-2fe), ti-13nb-13zr, temporal 21srx (ti-15mo-2.5nb-0.2si), tiadyne 1610 (ti-16nb-9.5hf) and Ti-15Mo, which are suitable for implanting into human body as implants, such as artificial bone, vascular stent, etc.
The biocompatibility of TiNi alloy is very good, and there are many medical examples using its shape memory effect and superelasticity. Such as thrombus filter, spinal orthopedic rod, dental orthopedic wire, vascular stent, bone plate, intramedullary needle, artificial joint, contraceptive device, heart repair components, artificial kidney micropump, etc.
Titanium alloy products can be obtained by die casting and machining. The melting temperature of titanium alloy is very high, and the requirement for die steel is also high. There are many machining methods for titanium alloy, including turning, milling, boring, drilling, grinding, tapping, sawing, EDM and so on.
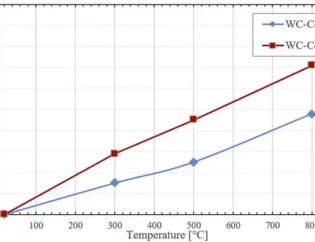
The machinability of titanium alloy is also poor. When cutting titanium alloy, the cutting force is only slightly higher than that of steel with the same hardness, but the thermal conductivity of most titanium alloys is very low, which is only 1 / 7 of that of steel and 1 / 16 of that of aluminum. Therefore, the heat generated by cutting will not disperse rapidly and gather in the cutting area, resulting in rapid wear, collapse and chip accretion of the cutting edge.